Benefits of inventory management

With the booming of e-commerce, the multi-channel sales model is the current trend nowadays. However, this is also a challenge for businesses in this era to synchronize and update inventory accurately, while their products are being sold in many different channels. Effective inventory management is one of the important factors for the success of any business. Here are several benefits of inventory management:
- Balance the number of necessary goods in the warehouse: Knowing exactly how much stock is in your inventory, combined with predictions for future demand, you can avoid holding too much or too little stock.
- Optimize goods rotation: Managing the shelf life of the products in your warehouse will help you adjust your sales strategy in time to speed up the goods’ rotation process. If a product stays in the warehouse for too long, it might lead to expiration or damage that causes property loss.
- Retain customers: No customer wants to return to a store where their desired items are always sold out. This is the reason why good inventory management and a reasonable restocking plan will help you retain your customers.
- Analysis and business planning: A detailed record of your inventory over the years will help you easily predict customer demand, keep inventory suitable and sufficient for each period.
- Increase the efficiency of capital use: Knowing the real-time quantity of goods in stock will help managers easily plan the schedule for stock in/stock out, thereby making more rational use of capital flows.
Boxme offers multi-channel management solutions with inventory, order and shipment management for business wishing to extend their retail network. Consult with us NOW.
Common inventory management method
There are many effective inventory management methods, of which the most commonly used are ABC and XYZ analysis.
The inventory management method using ABC and XYZ analysis is designed to review and adjust each item with different product codes, called Stock-keeping units (SKUs).
ABC analysis: Determine the consumption value
The ABC inventory method determines the consumption value of goods and specifies the level from A to C. Most companies have different categories to manage their inventory, and all items must be valued for efficient warehouse management. The ABC method makes it easy for businesses to classify goods by consumption value and business performance, thus building a plan to forecast, prepare and control the stock for each product category.
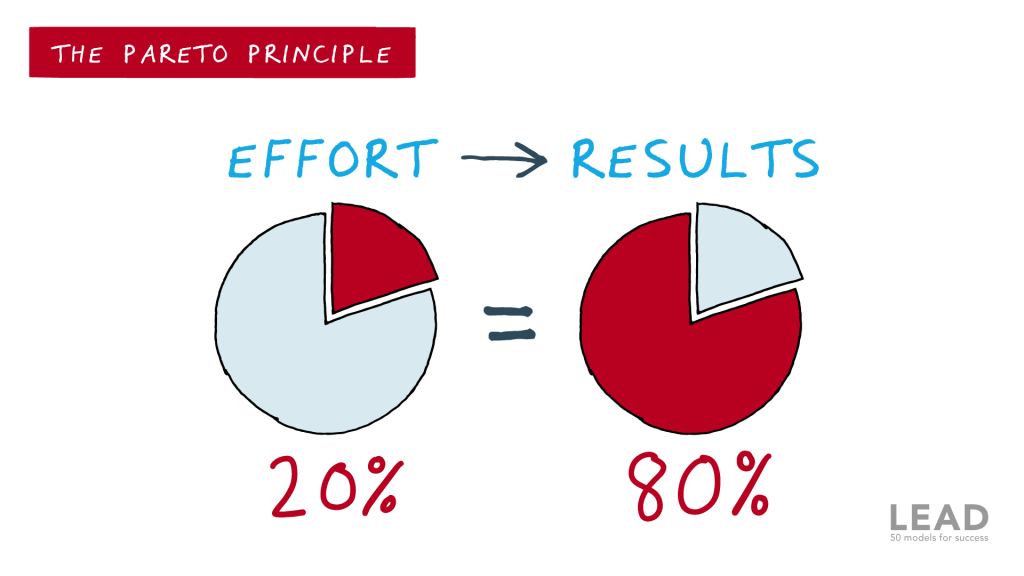
The origin of this method is the Pareto principle: 80% of the consequences come from 20% of the causes. This means that only 20% of goods bring in 80% of revenue. To put it simply, effectively controlling this 20% of goods will affect 80% of the whole system.
Accordingly, goods will be divided into 3 categories based on consumption value:
- Category A: goods with high value and a large contribution to revenue, accounting for 70-80% of sales and 10% of total goods output. This group is high refinement best-sellers so it needs to be stocked continuously.
- Category B: items with average consumption value, bringing in about 15-20% of revenue for the business.
- Category C: Low-value goods with a low contribution to revenue, accounting for only 5-10% of revenue but up to 40% of total goods output.
How to apply ABC analysis in inventory management?
ABC analysis helps businesses allocate funds appropriately. At the same time, inventory management methods must be compatible with each product group.
The funds allocated to buy A products should be more than C products, invested in sales and marketing activities the maximize profit. Group A products should also be prioritized in arrangement and supervision to ensure that supply never runs short. Predictions for A products in terms of demand, price, sales should be made to assure business efficiency.
ABC analysis helps determine the value of each product, thus appropriately allocating resources to maximize profits and minimize inventory risks.
XYZ analysis: evaluate demand stability
In pair with ABC analysis, the XYZ technique is used to identify the stability of goods, which is customer demand or sales in particular. Each item has a coefficient of sales variation, meaning the average deviation of actual sales compared to the sales target for each product, a coefficient of variation (CV) is calculated, which shows the average level of deviation (as a percentage) of the sales target for each period (year, quarter, month, week) compared to the average sales target for the item itself. If the CV is zero, it means that the sales targets for each period are the same. The bigger the CV number, the more unstable the sales target for this item. Accordingly, XYZ analysis in inventory management is classified as follows:
- X has a high level of demand stability and a low CV (less than 15%). Therefore, businesses can purchase a similar quantity to the previous period to avoid excess inventory.
- Y is an average level of demand stability which is seasonal (from 15-50%). Therefore, businesses need to consider the quantity before buying.
- Z has unpredictable demand with the CV being more than 50%, so businesses need to carefully examine the market before making any decisions.
Combination of ABC and XYZ analysis
In order to manage inventory and make accurate forecasts, businesses should use a combination of ABC and XYZ inventory analysis methods. Accordingly, when combining the two methods, we have the following table:
|
AX High consumption value Stable demandReliable forecast |
AY High consumption valuePredictable demandLess reliable forecast |
AZ High consumption valueUnpredictable demandUnreliable forecast |
|
BX Average consumption valueStable demandReliable forecast |
BY Average consumption valuePredictable demandLess reliable forecast |
BZ Average consumption valueUnpredictable demandUnreliable forecast |
|
CX Low consumption value Stable demandReliable forecast |
CY Low consumption value Predictable demandLess reliable forecast |
CZ Low consumption valueUnpredictable demandUnreliable forecast |
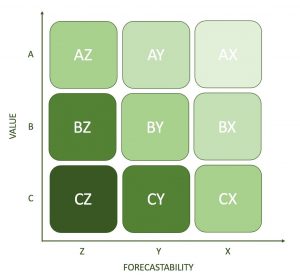
Based on this table, we can conclude that groups A and B support stability in the capital turnover of the business. Therefore, these two groups should be prioritized for storage and ready for dispatch anytime a transaction arises.
The AX and BX groups have a stable demand and bring great value to the business, so the number of goods in stock should be sufficient with a slight variation depending on the current situation.
Although the AY and BY groups ensure fast capital turnover, it is difficult to manage inventory. Therefore, enterprises must always have a contingency plan for goods in case the demand suddenly increases.
Group AZ and BZ have a high potential for sales but are difficult to forecast. Enterprises are recommended to control their inventory carefully to keep balance with the market demand.
In contrast, Group C does not bring in great value to the company. Therefore, businesses need to limit risks from this group.
CX group: businesses can reduce the number of goods in stock gradually over time.
CY group: businesses should only keep a small amount of these products, depending on current demand and the financial situation.
CZ Group: businesses should consider eliminating this group to limit the risk of overstocking which will affect revenue.
The combination of ABC and XYZ analysis methods helps businesses to improve inventory management and sales forecast. On the other hand, they can also take the initiative in planning future strategies and sourcing suppliers thanks to these analyses.
–> You might be interested in:
How To Speed Up Your E-Commerce Order Fulfillment
Which One Is The Best Warehouse Management Strategy: FIFO, FEFO Or LIFO?
Boxme is the premier cross-border e-Commerce fulfillment network in Southeast Asia, enabling world-wide merchants to sell online into this region without needing to establish a local presence. We deliver our services by aggregating and operating a one-stop value chain of logistic professions including: International shipping, customs clearance, warehousing, connection to local marketplaces, pick and pack, last-mile delivery, local payment collection and oversea remittance.